Large Intestine: Clostridioides difficile Colitis
Clostridioides difficile Colitis
Definitions
- Formerly “Clostridium difficile”
- Clostridioides difficile Colitis – Colon Infection Due to Clostridioides difficile Bacteria
- Clostridioides difficile Enteritis – Small Intestine Infection Due to Clostridioides difficile Bacteria
Basics
- Gram Positive, Spore-Forming Bacillus
- Transmission: Fecal-Oral
- Readily Cultured in the Hospital Environment
- Produces Two Exotoxins
- Toxin A & Toxin B
- Mediates Diarrhea & Colitis
- NAP1/BI/027 Strain – Hypervirulent/Epidemic Strain Associated with Multiple Outbreaks
- Most Common Site: Distal Colon
- Mucosal Disease with PMN Inflammation of Mucosa & Submucosa
- Exterior May Appear Normal at Time of Surgery Despite Aggressive Disease
Risk Factors
- ABX Use – Most Common Cause
- Most Commonly Implicated ABX: Clindamycin #1, Fluoroquinolones & Cephalosporins
- Typically Occur within 2 Weeks of Use but Can Occur > 3-5 Weeks After
- Age > 65
- Hospitalization & ICU Stay
- Severe Comorbid Illness
- Female Gender
- Gastric Acid Suppression
- Enteral Feeding
- GI Surgery
- Obesity
- IBD
- Chemotherapy
Presentation
- Symptoms:
- Watery Diarrhea (≥ 3 Stools/24 Hours)
- May Have Mucous or Occult Blood
- Abdominal Pain
- Fever
- Nausea
- Watery Diarrhea (≥ 3 Stools/24 Hours)
- Non-Severe Disease – Stable, Afebrile & Mild Symptoms with WBC ≤ 15,000 cells/dL
- Severe Disease – Symptomatic with Fever, WBC > 15,000 cells/mL or Cr ≥ 1.5 mg/dL
- Fulminant Disease – Characterized by Ileus, Hypotension/Shock or Megacolon
- Toxic Megacolon – *See Large Intestine: Toxic Megacolon
- Recurrent Disease – Recurrence of Symptoms within 2-8 Weeks After Treatment Stopped
- Must Have Seen Resolution of Symptoms While On Appropriate Therapy
Diagnosis
- Dx: Stool Test for Toxin A/B by ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunoassay)
- Other Options with Higher Sensitivity:
- NAAT (Nucleic Acid Amplification Testing)
- Toxigenic Culture
- Glutamate Dehydrogenase Stool Test
- Other Options with Higher Sensitivity:
- Colonoscopy May Show Pseudomembranes (Pseudomembranous Colitis) – Suggestive but Not Diagnostic
ABX Options & Dosing
- Vancomycin
- Oral 125 mg – Every 6 Hours for 10 Days
- High-Dose: Oral 500 mg Every 6 Hours
- Not Given IV (Does Not Cross GI Membrane)
- Metronidazole (Flagyl)
- Oral 500 mg – Every 8 Hours for 10 Days
- IV 500 mg – Every 8 Hours for 10 Days
- Fidaxomicin
- Newer Expensive Agent
- Oral 200 mg – Every 12 Hours for 10 Days
Treatment
- Treatment Options are Controversial & Debated
- Non-Severe/Severe Disease:
- Initial Episode: Vancomycin
- Other Options:
- Fidaxomicin
- Metronidazole – Only if Non-Severe
- Other Options:
- First Recurrence:
- Previously on Vancomycin: Vancomycin (Pulse & Taper) or Fidaxomicin
- Previously on Metronidazole or Fidaxomicin: Vancomycin
- Options for Subsequent Recurrences/Refractory Disease:
- Fecal Microbiota Transplant – Many Prefer if Available
- Vancomycin (Pulse & Taper)
- Vancomycin Followed by Rifaximin
- Fidaxomicin
- Initial Episode: Vancomycin
- Fulminant Disease:
- Tx: Combined ABX (High-Dose Vancomycin & IV Flagyl)
- Add Rectal Vancomycin Enema if Ileus Present
- Low Threshold for Surgery
- Surgery:
- Procedure: Total Colectomy & Ileostomy
- Segmental Resection Contraindicated Even if Believed to Be Confined to a Localized Area
- Indications:
- Absolute:
- Toxic Megacolon
- Perforation
- Peritonitis
- Relative:
- Fulminant Disease
- Medical Failure
- Worsening Clinical Course
- Absolute:
- Procedure: Total Colectomy & Ileostomy
Clostridioides difficile 1
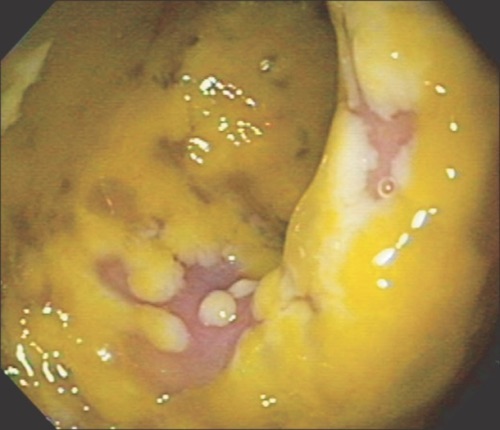
Pseudomembranous Colitis 2
References
- Archer J, CDC. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)
- Burke KE, Lamont JT. Clostridium difficile infection: a worldwide disease. Gut Liver. 2014 Jan;8(1):1-6. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)