Pancreas: Distal Pancreatectomy
Distal Pancreatectomy
Basics
- Resection of the Pancreatic Body & Tail to the Left of the SMA/SMV
- Indications:
- Chronic Pancreatitis with Small-Normal Ducts & Isolated to Tail
- Distal Cyst Concerning for Malignancy
- Distal Pancreatic Exocrine Cancer
- Distal PNET
- Metastases
- Trauma
- Preform Staging Laparoscopy If Concerned for Malignancy
Technique
- Retrograde Pancreatectomy
- Conventional Approach
- Procedure:
- Enter Lesser Sac – Divide Gastrocolic Ligament & Mobilize Omentum
- Mobilize Stomach – Ligate Gastrosplenic Ligament & Retract Cranially
- Mobilize Pancreatic Body/Tail – Spare Splenic Artery/Vein
- Transect Pancreas
- Consider Splenic Resection
- If for Malignancy – Send Tissue from Transection Margin for Frozen Section
- Radical Antegrade Modular Pancreaticosplenectomy (RAMPS) Procedure
- Provides More Extensive Lymph Node Dissection
- Procedure:
- Early Transection of Pancreas & Splenic Vessels
- Celiac Node Dissection
- Dissect Laterally
- Resects Distal Pancreas & Spleen
Spleen Management
- Always Vaccinate Preoperatively (Splenectomy is Commonly Performed)
- Concurrent Splenectomy
- Indications: High-Concern for Malignancy
- Chronic Pancreatitis – Consider Preserving Although May Be Very Difficult with Inflammatory Adherence to Splenic Vein
- Ligate: Splenic Artery (First), Then IMV & Finally Splenic Vein
- May Preserve IMV if it is Proximal to Lesion or Enters SMV
- Indications: High-Concern for Malignancy
- Spleen Preserving
- Indications: Benign or Cystic Mass
- Ligate: Individual Branches off Splenic Artery/Vein & IMV
- May Preserve IMV if it is Proximal to Lesion or Enters SMV
Complications
- Pancreatic Fistula (Most Common) (30-40%)
- Related More to Patient-Factors Than Operative-Technique
- Risk Factors: Age ≥ 60, Obesity, Malnutrition, Absence of Epidural, Nonmalignant Pathology, Concomitant Splenectomy or Vascular Reconstruction
- Not Impacted by Method of Resection, etc.
- Endocrine Insufficiency – New-Onset DM
- Higher Risk if Preformed for Pancreatitis
- Splenic Vein Thrombosis
- Bleeding
- Infection/Abscess
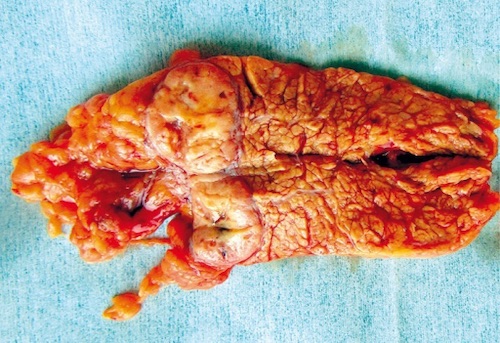
Distal Pancreatectomy 1
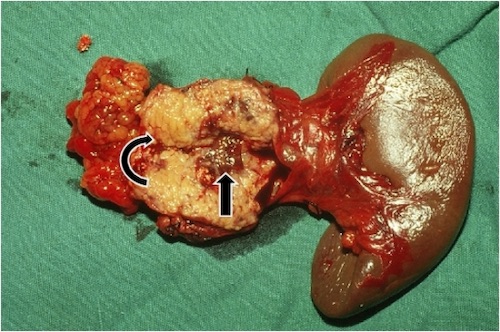
Distal Pancreatectomy with Concurrent Splenectomy 2
References
- Kusnierz K, Mrowiec S, Lampe P. Results of surgical management of renal cell carcinoma metastatic to the pancreas. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2015;19(1):54-9. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-3.0)
- Machado NO. Pancreaticopleural fistula: revisited. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2012;2012:815476. (License: CC BY-3.0)