Endocrine: Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) Syndrome
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) Syndromes
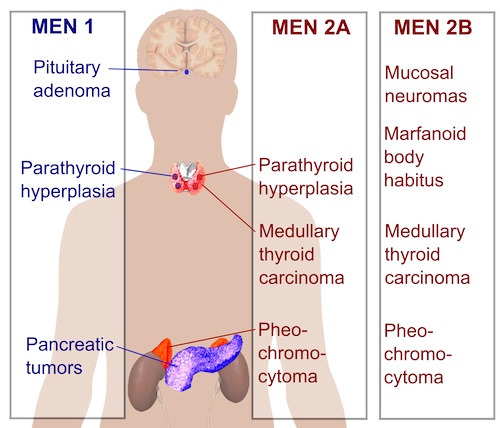
MEN I (Wermer Syndrome)
- Mutation: MENIN Gene (Tumor Suppressor Gene on Chromosome 11) Mn
- Autosomal Dominant
- Primary Associations: Mn
- Primary Hyperparathyroidism (90-100% – Most Common Manifestation)
- Usually Affects Multiple Glands (Asynchronous & Asymmetric)
- Each Gland is Considered a Monoclonal Lesion – Hyperplastic or Adenomatous
- Pancreatic Islet Cell Tumors (60-70%)
- Most Common Functional Tumor: Gastrinoma
- Gastrinoma & Nonfunctional Tumors Have Similar Prevalence
- Pituitary Adenoma (15-42%)
- Most Common: Lactotroph/Prolactinoma
- Primary Hyperparathyroidism (90-100% – Most Common Manifestation)
- Other Associations:
- Adrenocortical Tumors
- Carcinoid Tumors (Most Common Site in MEN I: Thymus)
- Lipoma
- Leiomyoma
- Meningioma
- Angiofibroma
- Spinal Cord Ependymomas
- Pheochromocytoma or Paraganglioma – Very Rare & Much More Common in MEN II
MEN IIA (MEN II/Sipple Syndrome)
- Much More Common Than Type 2B (90% of MEN II Cases)
- Mutation: RET (Proto-Oncogene on Chromosome 10)
- Autosomal Dominant
- Primary Associations:
- Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (Almost 100% – Most Common Manifestation)
- Pheochromocytoma (40-50%)
- Parathyroid Hyperplasia (10-25%)
- Other Associations:
- Cutaneous Lichen Amyloidosis – Pruritic, Scaly & Pigmented Lesions on Extensor Surfaces or Intrascapular Region
- Hirschsprung Disease
- Subtypes:
- Classical MEN 2A – Only the 3 Primary Associations
- MEN 2A with Cutaneous Lichen Amyloidosis
- MEN 2A with Hirschsprung Disease
- Familial Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma – High-Risk for MTC but Not the Other Manifestations
MEN IIB (MEN III)
- Mutation: RET (Proto-Oncogene on Chromosome 10)
- Autosomal Dominant
- Primary Associations:
- Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (Almost 100% – Most Common Manifestation)
- Pheochromocytoma (40-50%)
- Other Associations:
- Mucosal Neuromas – Involving Lips & Tongue
- Marfan Habitus – Tall Stature, Long Limbs & Hyperlaxity
- No Aortic Abnormalities Which are Seen in Marfan Syndrome
- Intestinal Autonomic Ganglion Dysfunction – Leads to Megacolon
MEN IV (MEN X)
- Mutation: CDNK1B (Tumor Suppressor Gene)
- Autosomal Dominant
- Primary Associations:
- Primary Hyperparathyroidism
- Pituitary Adenoma
- Other Associations:
- Adrenal Tumors
- Kidney Tumors
- Reproductive Organ Tumors (Testicular Cancer or Cervical Neuroendocrine Tumors)
MEN Syndromes 1
MEN Clinical Course & Management
Most Common Initial Manifestation
- MEN I: Primary Hyperparathyroidism
- MEN IIA/IIB: Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
Most Common Cause of Death
- MEN I: Nonfunctional Pancreatic Tumor Malignancy
- MEN IIA/IIB: Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma
- MEN IIA Risk: 9.7%
- MEN IIB Risk: 50%
Screening Tests
- Indications:
- All Diagnosed Patients Should be Screened for Other Associated Tumors
- All First/Second Degree Family Members Should be Screened for Other Associated Tumors & Gene Mutations
- MEN I:
- Metabolic Panel (Including Calcium)
- Gastrin Level
- Prolactin Level
- MEN IIA/IIB:
- Metabolic Panel (Including Calcium) – Not Needed for Type IIB
- Calcitonin Level & Thyroid US
- Plasma Metanephrines
First Manifestation to Surgically Correct if Multiple are Concurrent
- MEN I: Primary Hyperparathyroidism
- MEN IIA/IIB: Pheochromocytoma
Prophylactic Thyroidectomy in MEN IIA/IIB
- MEN IIA:
- Low/Moderate-Risk Mutations: Start Clinical Monitoring by 3-5 Years of Age
- High-Risk Mutations: Thyroidectomy Before Age 5 Years
- MEN IIB: Thyroidectomy in First Year of Life Mn
Mnemonics
MEN I Mutation & Chromosome
- MEN-I: MEN-I-n & I-I (Eleven)
MEN Disease Associations
- P’s (3>2>1) & M’s (0>1>2-3) to Total 3 for Each
- I: 3 P’s & 0 M’s (Total 3)
- IIA: 2 P’s & 1 M (Total 3)
- IIB: 1 P & 2-3 M’s (Total 3)
- When Differentiating the P’s
- I P’s: Close to Midline (Pituitary, Pancreas & Parathyroid)
- II P’s: Have 2 Sides (Parathyroid & Pheochromocytoma/Adrenals)
Prophylactic Thyroidectomy in MEN IIA/IIB
- B-Bad: Worse Prognosis & Needs Surgery Earlier
References
- Haggstrom M. Wikimedia Commons. (License: Public Domain)