Trauma: Orthopedic Fractures
Orthopedic Fractures
Gustilo Classification of Open Fractures
- Type I: Wound ≤ 1 cm & Minimal Soft Tissue Damage/Contamination
- Type II: Wound 1-10 cm or Moderate Soft Tissue Damage
- Type III:
- A: Wound > 10 cm, Extensive Soft Tissue Damage or Contaminated
- Includes All Farm Injuries
- B: Extensive Periosteal Stripping or Requiring Soft Tissue Coverage
- C: Vascular Injury Requiring Repair
- A: Wound > 10 cm, Extensive Soft Tissue Damage or Contaminated
Initial Management
- Evaluation:
- Always Evaluate Neurovascular Status First
- If Fracture/Dislocation with Weak/No Pulse: Reduce and Reassess
- Still None: Surgical Vascular Repair
- Weak: CTA
- Irrigation & Debridement:
- Timing Within 24 Hours or As Soon As Possible if Contaminated
- Use NS at Low Pressure, 3 L Per Successive Gustilo Type (I: 3L, II: 6L, III: 9L)
- Antibiotics:
- Gustilo Type I/II: First Generation Cephalosporin (Ancef)
- Gustilo Type III: Add Gram Negative Coverage (Gentamicin)
- Severe Contamination or Vascular Injury: Add Anaerobic Coverage (Penicillin)
Fracture Repair
- Early Operative Fixation Best
- High ISS: Delay 2-4 Days
- Bony Stabilization Before Vascular Reconstruction
- If Extremity is Grossly Ischemic or Actively Hemorrhaging – Control with a Temporary Shunt & Fasciotomy Prior to Bony Stabilization & Then Vascular Reconstruction
- Options:
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)
- Types: IM Nail vs. Plating
- Generally Preferred
- Reduced Pulmonary Complications
- External Fixation (Ex-Fix)
- Indications: Extensive Soft Tissue Destruction, Contamination or Associated Vascular Injury
- Open Reduction and Internal Fixation (ORIF)
Throckmorton (John Thomas/JT) Sign
- Definition: When the Male Penis Points in the Direction of Unilateral Injury
- Classically Refers to Hip/Pelvic Fractures Seen on Plain Film XR
- Considered a Joke Term with No Real Diagnostic Utility
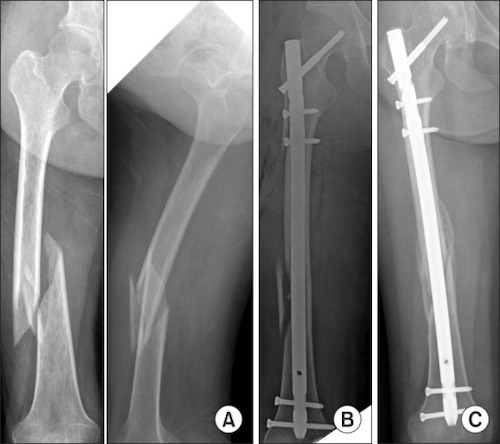
IM Nail 1
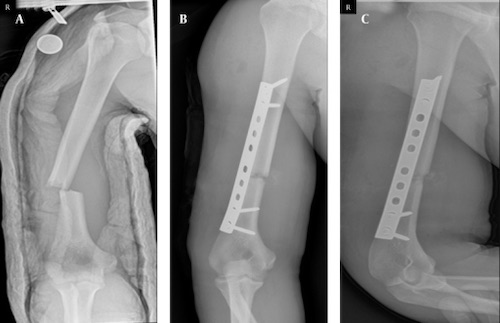
ORIF Plating 2
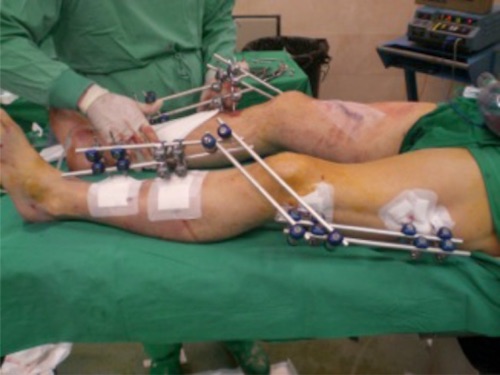
External Fixation 3
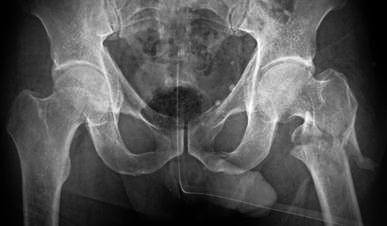
Throckmorton Sign 4
References
- Yun HH, Oh CH, Yi JW. Subtrochanteric femoral fracture during trochanteric nailing for the treatment of femoral shaft fracture. Clin Orthop Surg. 2013 Sep;5(3):230-4. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)
- Esmailiejah AA, Abbasian MR, Safdari F, Ashoori K. Treatment of Humeral Shaft Fractures: Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis Versus Open Reduction and Internal Fixation. Trauma Mon. 2015 Aug;20(3):e26271. (License: CC BY-NC-4.0)
- Guerado E, Bertrand ML, Valdes L, Cruz E, Cano JR. Resuscitation of Polytrauma Patients: The Management of Massive Skeletal Bleeding. Open Orthop J. 2015 Jul 31;9:283-95. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)
- Parmaksızoğlu F, Cansü E, Unal MB, Yener Ince A. Acute emergency tibialization of the fibula: reconstruction of a massive tibial defect in a type IIIC open fracture. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2013 Aug;8(2):127-31. (License: CC BY-4.0)