Pancreas: Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple Procedure)
Pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple Procedure)
Basics
- Resection of Pancreatic Head & Duodenum
- Avoid Preoperative Biliary Drainage (ERCP/Stent)
- Increased Risk of Wound Infection & Pancreatic Fistula
- No Improved Morbidity or Mortality
Indications
- Chronic Pancreatitis with Small-Normal Ducts & Isolated to Head
- Head Cyst Concerning for Malignancy
- Head Pancreatic Exocrine Cancer
- Head PNET
- Metastases
- Trauma (Never Emergent)
- Distal CBD Cholangiocarcinoma
- Periampullary Duodenal Adenocarcinoma
Unresectable Definition
Resection
- Pancreatic Head & Duodenum
- Gallbladder & CBD
- Gastric Antrum & Pylorus
- Proximal Jejunum (15 cm)
Classic Pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Preform an Initial Staging Laparoscopy If Concerned for Malignancy
- Mobilize Duodenum, Pancreatic Head & Stomach
- Requires Kocher Maneuver
- Isolate Portal Structures
- Divide Right Gastric Artery & GDA
- Cholecystectomy & Common Hepatic Duct Transection
- Transect Stomach 2 cm Proximal to Pylorus
- Mobilize Proximal Jejunum & Transect
- Transect Neck of Pancreas
- Transection Plane Created by Developing a Tunnel Anterior to SMV
- Retract Specimen Medially Off the SMV-Portal Vein Confluence
- Exposes Inferior Pancreaticoduodenal Arteries – Carefully Ligate Branches to Avoid Avulsion
- Reconstruction:
- Pancreaticojejunostomy (PJ)
- At Most Proximal Aspect
- Responsible for Majority of Postoperative Morbidity
- Hepaticojejunostomy (HJ)
- Distal to PJ Anastomosis to Prevent Backflow
- Gastrojejunostomy (GJ)
- ≥ 30-40 cm (Often 45-60 cm) Distally to Prevent Food Reflux into Biliary/Pancreatic Anastomoses
- Pancreaticojejunostomy (PJ)
Pylorus-Preserving Pancreaticoduodenectomy
- Preserves:
- Gastric Antrum & Pylorus
- Proximal Duodenum (3-4 cm)
- Contraindications: Involvement of First Portion of Duodenum, Pylorus or Antrum
- Comparison to Classic Whipple:
- Faster Procedure & Lower Blood Loss
- Often Preferred Method
- No Significant Difference in Outcomes
- Faster Procedure & Lower Blood Loss
Complications
- Gastroparesis (17%)
- Most Common Complication
- Tx: Reglan or Erythromycin
- Pancreatic Fistula (5-10%)
- Most Common Serious Complication
- High Mortality
- Bile Leak (1-3%)
- Bleeding
- Usually from GDA Leak
- Friable and Difficult to Control in OR
- Tx: Angioembolization
- Marginal Ulcer
- Tx: PPI
- Endocrine Insufficiency – New-Onset DM
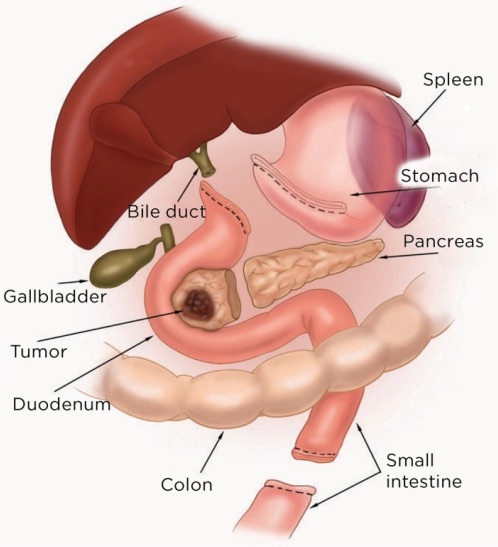
Pancreaticoduodenectomy Resection 1
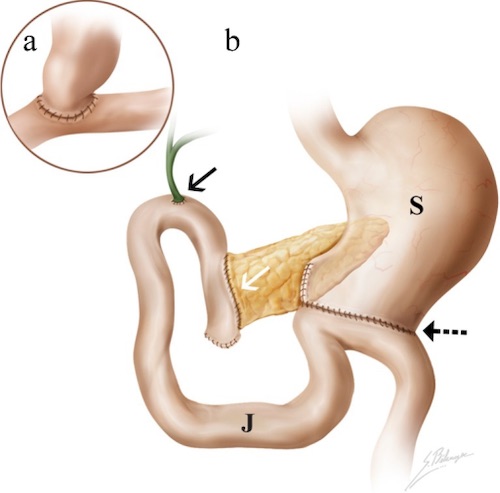
Pancreaticoduodenectomy Reconstruction 2
References
- Reynolds RB, Folloder J. Clinical Management of Pancreatic Cancer. J Adv Pract Oncol. 2014 Sep-Oct;5(5):356-64. (License: CC BY-2.0)
- Terrone DG, Lepanto L, Billiard JS, Olivié D, Murphy-Lavallée J, Vandenbroucke F, Tang A. A primer to common major gastrointestinal post-surgical anatomy on CT-a pictorial review. Insights Imaging. 2011 Dec;2(6):631-638. (License: CC BY-2.0)