Cardiothoracic Surgery: Parapneumonic Effusion & Empyema
Parapneumonic Effusion & Empyema
Definitions
- Parapneumonic Effusion – Pleural Fluid that Develops in Response to Adjacent Pneumonia
- Uncomplicated – Sterile Effusion
- Complicated – Infected Effusion
- Empyema – Purulent Fluid within the Pleural Cavity
- The Majority are Due to Infection of a Parapneumonic Effusion
- *Can Be Considered a Subclass of Complicated Parapneumonic Effusion if Develops in Response to Adjacent Pneumonia
Rates
- Rate of Parapneumonic Effusion in Hospitalized Patients with Pneumonia: 20-40%
- Rate of Empyema in Hospitalized Patients with Parapneumonic Effusion: 5-10%
- Empyema Mortality of Hospitalized Patients: 15%
Stages/Phases
- Stage I: Uncomplicated/Exudative
- Timing: < 5 Days
- Sterile Free-Flowing Fluid Develops from Increased Capillary Permeability
- Stage II: Complicated/Fibrinopurulent
- Timing: > 5 Days
- Bacteria Enter the Fluid & Cause Inflammation
- Stage III: Complicated/Organizing
- Timing: > 2-3 Weeks
- Fibroblasts Form a Fibrous Pleural Peel Causing Lung Trapping
- Usually Resolves After 3-6 Months but Scarring Can Be Permanent
Diagnosis
- Indications for Thoracentesis:
- Size > 100 cc
- Loculations
- Associated Findings:
- Uncomplicated Parapneumonic Effusion:
- Size < 100 cc
- No Loculations
- Complicated Parapneumonic Effusion:
- Positive Culture/Gram Stain
- pH < 7.20
- Large Size > 1,000 cc
- Loculations
- Thickened Pleura
- Air Bubbles within Effusion
- Empyema:
- Frank Purulence on Thoracentesis
- Uncomplicated Parapneumonic Effusion:
Treatment
- Uncomplicated Parapneumonic Effusion: Antibiotics
- Complicated Parapneumonic Effusion or Empyema: Antibiotics & Chest Tube Drainage
- May Require Multiple Chest Tubes for Adequate Drainage
- May Also Consider Intrapleural tPA/DNase
- If Fails or Have Significant Organization: Surgical Decortication
- Approach: Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (VATS) or Open Thoracotomy
- If Not a Surgical Candidate: Eloesser Flap (Open Thoracic Window)
- May Require Multiple Chest Tubes for Adequate Drainage
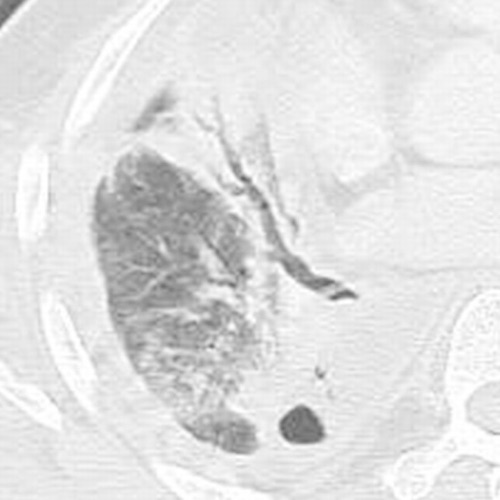
Empyema on CT 1
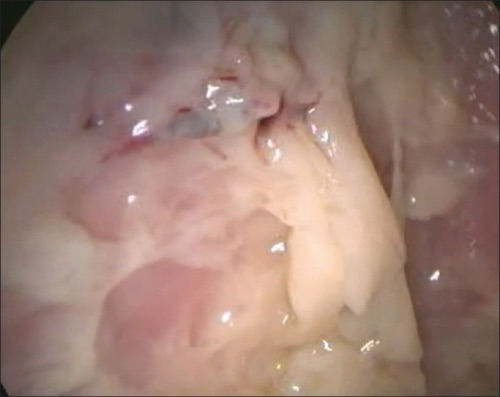
Empyema with Necrotic Purulent Debris on Thoracoscopy 2
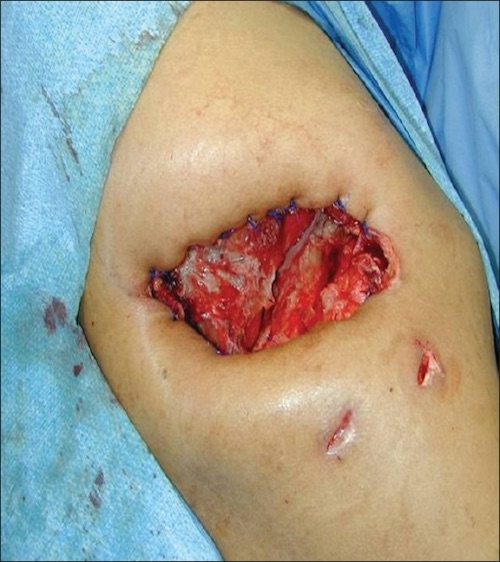
Eloesser Flap 3
References
- Tsubakimoto M, Murayama S, Iraha R, Kamiya H, Tsuchiya N, Yamashiro T. Can Peripheral Bronchopleural Fistula Demonstrated on Computed Tomography be Treated Conservatively? A Retrospective Analysis. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2016 Jan-Feb;40(1):86-90. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-4.0)
- Patil CB, Dixit R, Gupta R, Gupta N, Indushekar V. Thoracoscopic evaluation of 129 cases having undiagnosed exudative pleural effusions. Lung India. 2016 Sep-Oct;33(5):502-6. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)
- Wait MA, Beckles DL, Paul M, Hotze M, Dimaio MJ. Thoracoscopic management of empyema thoracis. J Minim Access Surg. 2007 Oct;3(4):141-8. (License: CC BY-2.0)