Surgical Critical Care: Tracheostomy – Complications
Bleeding
Early Minor Bleeding
- Bleeding from Local Trauma to Superficial Veins
- Occurs within First 48 Hours
- Treatment:
- Silver Nitrate
- Packing Petroleum Gauze
- Packing Surgicel Gauze
- Injection of Lidocaine with Epinephrine
Tracheo-Innominate Fistula (TIF)
- Fistula Between Innominate Artery & Trachea
- Causes Rapid Exsanguination
- Occurs After 48 Hours
- 50% are Heralded by a Sentinel Bleed
- Most Common Causes:
- Prolonged Exposure to Overinflated Cuff Pressures
- Abnormally Low Tracheostomy Placement
- Repetitive Head Movements Causing Repeated Contact
- Treatment:
- Initial: Pressure
- Overinflate Cuff – Pressure Against Sternum
- Utley Maneuver – Finger Through Incision into Pretracheal Space to Apply Anterior Pressure Against Sternum (Not into the Trachea Itself)
- Small Sentinel Bleed: Preform Bronchoscopy in OR to Examine
- Definitive Treatment: Median Sternotomy & Innominate Artery Ligation
- Primarily Repair Trachea and Buttress with Viable Tissue
- Failure to Ligate Has High Risk for Re-Fistulation
- Do Not Use Interposition Graft (Will Become Infected)
- Some Have Suggested Use of Endovascular Stents if Prohibitively High Surgical Risk
- 10% of Patients Experience a Neurologic Event After Ligation
- Initial: Pressure
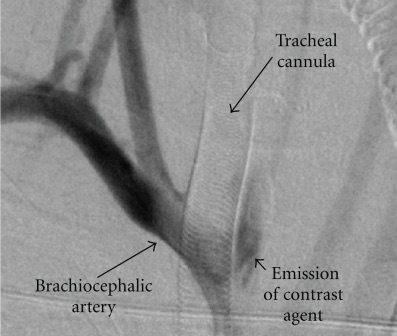
Tracheoinominate Fistula on Angiogram 1
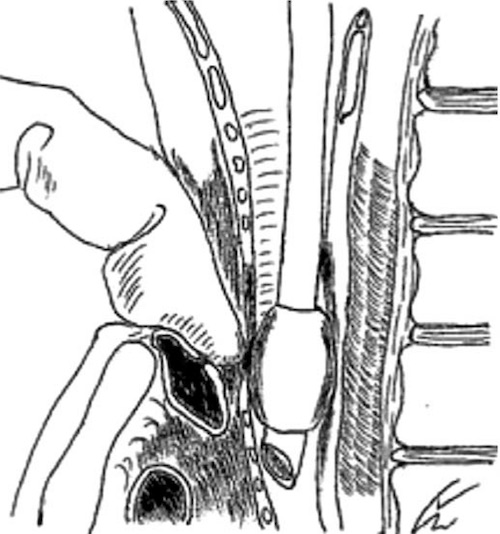
Utley Maneuver 2
Other Complications
Tracheoesophageal Fistula (TEF)
- Risk Factors:
- High Cuff Pressure (#1)
- Concomitant Nasogastric Tube
- Excessive Motion
- Presentation:
- Ono’s Sign – Uncontrolled Coughing After Swallowing
- Respiratory Distress
- Recurrent Pneumonia
- Treatment:
- Initial Management: Large Volume Cuff Endotracheal Tube Below the Fistula
- Prevent Aspiration
- Definitive Treatment: Surgical Repair (Primary Repair vs Resection)
- If Not a Surgical Candidate: Combination Tracheal & Esophageal Stenting
- Tracheal Stent Before Esophageal Stent – Esophageal Expansion May Compress Trachea
- Initial Management: Large Volume Cuff Endotracheal Tube Below the Fistula
Tracheostomy Obstruction
- Causes:
- Mucous Plugging
- Clotted Blood
- Passage into A False Lumen (Paratracheal Soft Tissue)
- Tube Angulation
- Presentation: Acute Respiratory Deterioration
- Treatment:
- Initial Attempt: Suctioning of Tracheostomy Tube
- If Fails: Exchange Inner Cannula
Dislodgement/Accidental Decannulation
- Emergency if Occurs within First 7 Days
- Without a Mature Tract Replacement Could Cause a False Tract
- Presentation: Acute Respiratory Distress & Subcutaneous Emphysema
- Treatment: Endotracheal Intubation
- If Stable May Consider Bronchoscopic-Guided Replacement in Experienced Hands
Tracheal Stenosis
- The Most Common Late Complication
- Almost All Have Some Degree of Stenosis
- Only 3-12% Have Clinically Significant Stenosis
- Typically Seen at the Level of the Stoma
- Often Asymptomatic Until Lumen Reduced to < 5 mm (25-50% of Original Diameter)
- Presentation:
- Elevated Peak Airway Pressures if Infra-Stomal Stenosis
- Dyspnea, Stridor & Respiratory Failure After Decannulation
- Grading:
- Grade I: ≤ 50%
- Grade II: 51-70%
- Grade III: 71-99%
- Grade IV: 100%
- Complexity:
- Simple: < 1 cm, Granulation Tissue, Web-Like Lesion, Concentric or No Involvement of Tracheal Wall
- Complex: > 1 cm, Scarring or Presence of Tracheomalacia
- Diagnosis: Bronchoscopy
- Treatment:
- Simple: Bronchoscopic Serial Dilation
- Possibly Bronchoscopic Resection or Laser Ablation
- Complex: Tracheal Resection (Up to 6 cm) & End-to-End Anastomosis
- Simple: Bronchoscopic Serial Dilation
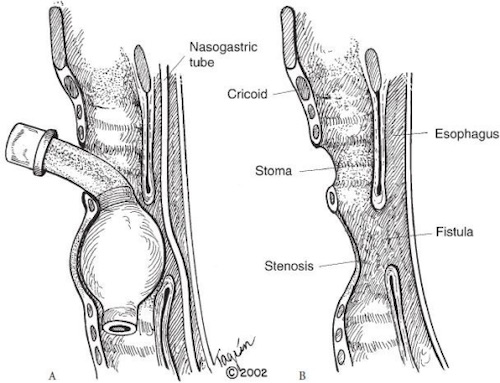
Tracheoesophageal Fistula 3
References
- Richter T, Gottschlich B, Sutarski S, Müller R, Ragaller M. Late life-threatening hemorrhage after percutaneous tracheostomy. Int J Otolaryngol. 2011;2011:890380. (License: CC BY-3.0)
- Kim JH, Lee JY, Cho HR, Lee JS, Ryu JM. A tracheoinominate artery fistula presenting with massive hemorrhage in a 13-year-old boy. Ped Emerg Med. 2015;2(2):89-92. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)
- Paraschiv M. Tracheoesophageal fistula–a complication of prolonged tracheal intubation. J Med Life. 2014 Oct-Dec;7(4):516-21. (License: CC BY-2.0)