Urology: Anatomy & Physiology
Urinary Tract
Urinary Tract
- Upper Urinary Tract:
- Kidney
- Ureter: Draining Urine from the Kidney/Renal Pelvis to the Bladder
- Lower Urinary Tract:
- Bladder
- Urethra: Empties Urine
- Fascia Surrounding the Kidney & Perirenal Fat
- Anterior & Posterior Leaves
- Fuse Medially, Laterally & Superiorly
- Remains Open Inferiorly (Ureter & Gonadal Vessels Exit)
- Structures (Anterior to Posterior): Mn
- Renal Vein > Renal Artery > Renal Pelvis
- Right Renal Artery: Travels Posterior to IVC
- Left Renal Vein: Travels Anterior to Aorta
- Can Be Ligated Distally Due to High Collaterals
- Right Too Short & Lacks Collaterals
- Branches of Left Renal Vein: (To IVC on the Right)
- Gonadal Vein
- Adrenal Vein
- Second Lumbar Vein
- Can Be Ligated Distally Due to High Collaterals
- Tubular Structures Draining Urine from the Kidney/Renal Pelvis to the Bladder
- Diameter: 2-6 mm
- Length: 20-30 cm
- Abdominal Ureter: Descends Along the Anterior Edge of the Psoas Muscle to the Pelvic Brim
- Close Relationship to the Ipsilateral Colon
- At the Pelvic Brim They Cross Over the Common Iliac Vessels (Generally Where the Vessels Bifurcates into Internal/External)
- Pelvic Ureter: Descend Along the Side Walls of the Pelvis (From the Pelvic Brim to the Bladder)
- Enters the Posterior Wall of the Bladder & Drains into the Trigone
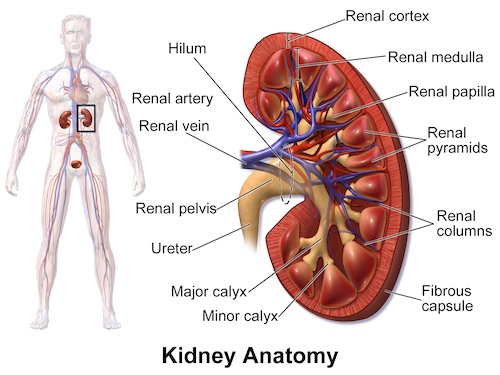
Kidney & Renal Hilum 1
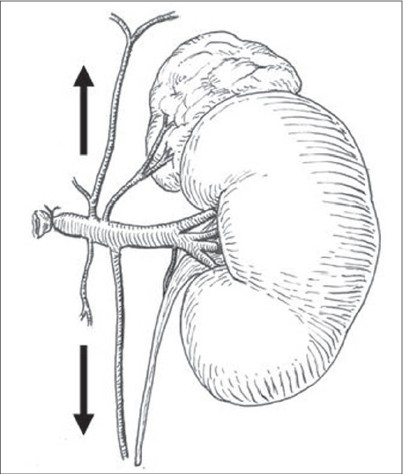
Branches of the Left Renal Vein: Phrenic, Adrenal, Second Lumbar, Gonadal & Ureteral 2
Male Genitalia
Male Reproductive System
- Testis – Produce Sperm in the Seminiferous Tubules & Secrete Hormones
- Epididymis – Mature Sperm & Transfer from the Testis to Vas Deferens
- Vas Deferens (Ductus Deferens) – Transfers Sperm to the Ejaculatory Duct
- Accessory Glands:
- Seminal Vesicles – Located Behind the Bladder & Secretes Fluid to Compose Semen
- Prostate Gland – Located Below the Bladder Around the Urethra & Produces Fluid to Compose Semen
- Bulbourethral Gland – Located at the Base of the Penis, Posterolateral to the Membranous Portion of the Urethra & Produces Pre-Ejaculate Fluid
- Ejaculatory Duct – Passes Semen Through the Prostate into the Urethra During Ejaculation
- Formed by the Vas Deferens & Seminal Vesicles
- External Organs:
- Penis
- Scrotum
Gonadal Vasculature
- Gonadal Arteries: From Aorta
- Gonadal Veins
- Left: To Left Renal Vein
- Right: To IVC
Lymphatics of the Testicles
- Right: Paracaval & Interaortocaval Lymph Nodes
- Left: Para-Aortic Lymph Nodes
Spermatic Cord Contents
- Testicular Artery
- Pampiniform Plexus
- Vas Deferens
- Cremasteric Muscle
- Ilioinguinal Nerve
- Genital Branch of Genitofemoral Nerve
Male Urethra Segments
- Posterior Urethra:
- Prostatic (3 cm) – Through the Prostate Gland
- Membranous (1 cm) – Through the Urogenital Diaphragm/External Urethral Sphincter
- Anterior Urethra:
- Bulbar – The Root of the Penis
- Penile/Spongy (16 cm) – Through the Corpus Spongiosum
Penis Structure
- Three Columns:
- Corpora Cavernosa (x2) on Dorsal Side – Fills with Blood to Create an Erection
- Corpus Spongiosum (x1) on Ventral Side – Erectile Tissue Surrounding the Urethra
- Parts:
- Root of the Penis – Attached to the Body, Composed of the Crura & Urethral Bulb
- Body of the Penis – External Portion
- Glans Penis (Head) – Distal Bulbous End of the Penis
- Foreskin (Prepuce) – Fold of Tissue Covering the Glans Penis (Can Be Involved in Various Infections)
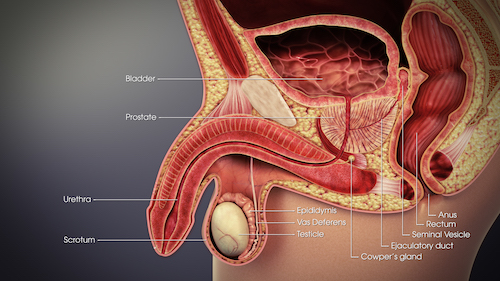
Male Reproductive System 3
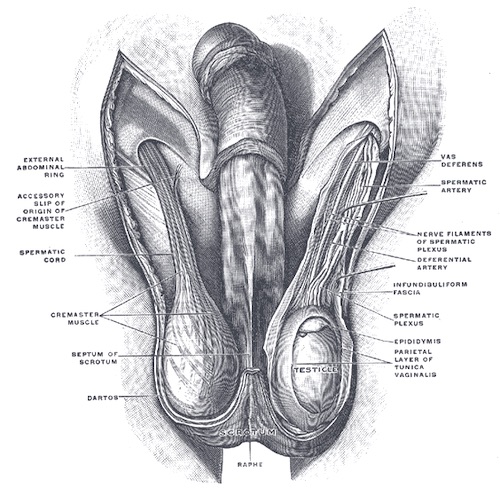
Scrotum & Spermatic Cord 4
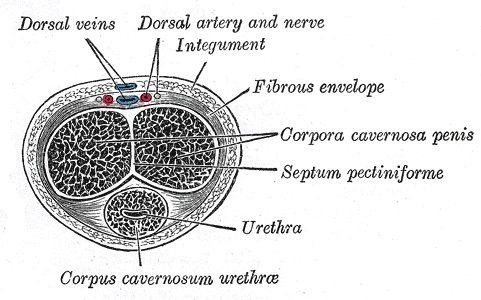
Penis Cross-Section 4
Mnemonics
Renal Hilum Structures (Anterior to Posterior)
- VAP: Vein-Artery-Pelvis
- VA-AP: Vein Anterior to Aorta, Artery Posterior to IVC
References
- Blaus B. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-3.0)
- Tröbs RB. Anatomical basis for Wilms tumor surgery. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg. 2009 Apr;14(2):50-4. (License: CC BY-2.0)
- ScientificAnimations.com. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)
- Gray H. Anatomy of the Human Body (1918). Public Domain.