Biliary Tract: Anatomy & Physiology
Anatomy
Normal Sizes
- CBD < 6-8 mm
- 10 mm After Cholecystectomy
- Increases 1 mm Every 10 Years After Age 60
- Gallbladder Wall < 4 mm
- Pancreatic Duct < 4 mm
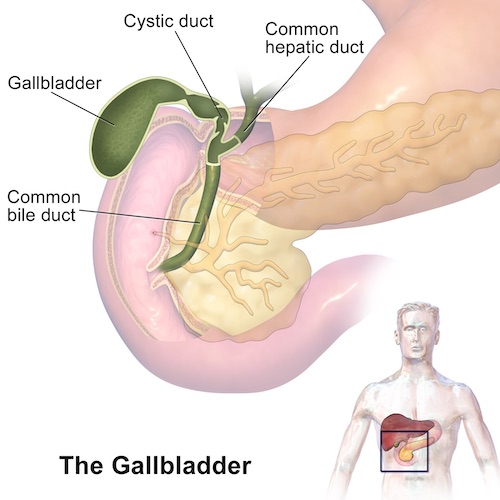
Gallbladder Anatomy
- Structure
- Fundus – Round Distal Projection
- Body – Largest Portion
- Neck – Tapered Portion Continuous with Cystic Duct
- Layers
- Mucosa – Columnar Epithelium
- No Submucosa
- Gallbladder Lies Beneath Liver Segments IV/V
Biliary Tract
- Left & Right Hepatic Ducts Combine to Form Common Hepatic Duct (CHD)
- Left Haptic Duct is Longer Than Right
- Left Haptic Duct is More Likely to Dilate in Distal Obstruction
- Cystic Duct Enters Common Hepatic Duct to Form Common Bile Duct (CBD)
- Heister Valve – Spiral Valves in Cystic Duct with No Valve Function
- CBD & Pancreatic Duct Unite Outside Duodenal Wall
- Traverse Wall as Single Duct
- Sphincter of Oddi
- Muscular Fibers within Wall of Duodenum Around Ampulla of Vater
- Components
- Sphincter Choledochus (Sphincter of Boyden) – Encircles CBD
- Sphincter Pancreaticus – Encircles Pancreatic Duct
- Interlocks with Sphincter Choledochus to form Figure-of-Eight
Accessory Structures
- Rokitansky-Aschoff Sinuses
- Epithelial Invaginations in Gallbladder Wall
- From Increased Pressure (Chronic Cholecystitis)
- Ducts of Luschka
- Accessory Bile Ducts in Gallbladder Fossa
- Can Leak After Cholecystectomy
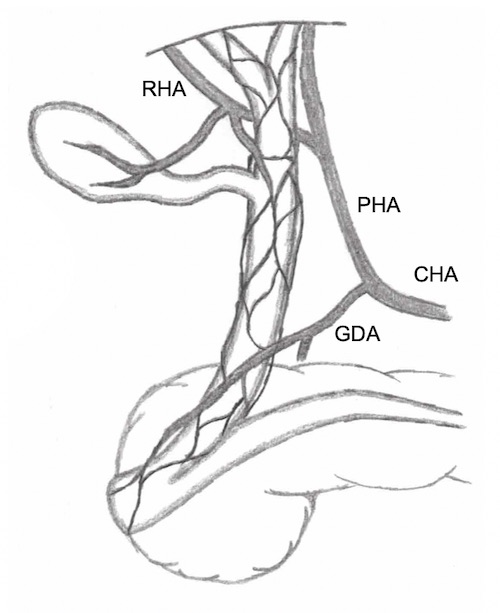
Vascular Supply
- Gallbladder
- Cystic Artery – Off Right Hepatic Artery
- Found in Triangle of Calot
- Branches: Superficial & Deep
- Cystic Vein – Into Right Branch of Portal Vein
- Cystic Artery – Off Right Hepatic Artery
- CBD
- Marginal Arteries at 3-o’clock and 9-o’clock on ERCP
- Supply
- Lateral Portion (Proximal): Right Hepatic Artery
- Medial Portion (Distal): GDA (Retroduodenal Branches)
Lymphatics
- Lie to the Right of CBD
Nerves
- Parasympathetics – Left Vagus Trunk (Anterior)
- Sympathetics – Splanchnic & Celiac Ganglions
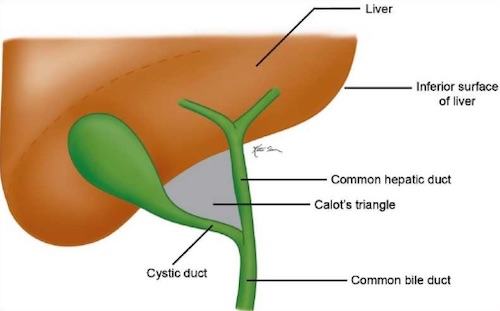
Triangle of Calot
- Borders:
- Lateral: Cystic Duct
- Medial: Common Hepatic Duct
- Superior: Liver
- Contents:
- Cystic Artery
- Node of Calot (Cystic Node)
- First Site of Mets
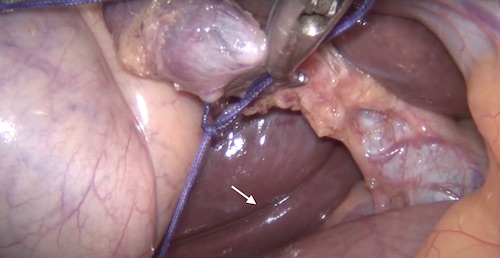
- Rouviere’s Sulcus – Naturally Occurring Cleft in the Right Lobe of the Liver, Anterior to Segment 1
- Used as Landmark to Begin Dissection of Calot’s Triangle
- Present in 80% of Normal Livers
Aberrant Anatomy
- Biliary System:
- Anatomic Variation Frequency: 30-40%
- Most Variable Course: Right Posterior Hepatic Duct
- Anomalies:
- Trifurcation: Right Posterior Joins with Right Anterior & Left Hepatic Ducts Together (10-11%)
- Crossover Anomaly: Right Posterior Joins with Left Hepatic Duct (11-15%)
- Most Common Anomaly
- Other Anomalies:
- Right Posterior Joins with Common Hepatic Duct (6%)
- Right Posterior Joins with Cystic Duct (2%)
- Right Hepatic Duct Drains into the Cystic Duct
- Accessory Hepatic Ducts
- *Multiple Different Classification Systems with Different Types Have Been Proposed
- Vascular System:
- Cystic Artery Origin Variations: Common Hepatic, Gastroduodenal or SMA
- Double Cystic Arteries Seen in 10%
Gallbladder & Biliary Tract Anatomy 1
Blood Supply of the Biliary Tract
Triangle of Calot 2
Rouviere’s Sulcus
Physiology
Bilirubin
- Production
- Hgb Breakdown > Heme > Biliverdin > Unconjugated Bilirubin
- Unconjugated Bilirubin
- Conjugated in Liver by Glucuronyl Transferase (Adds Glucuronic Acid)
- Conjugated Bilirubin
- Increased Water Solubility & Secreted in Bile
- Gut
- Conjugated Bilirubin > Urobilinogen > Stercobilinogen > Stercobilin
- Breakdown by Bacteria in Terminal Ileum
- Urobilinogen – Reabsorbed
- Stercobilin – Brown Color of Stool
- Conjugated Bilirubin > Urobilinogen > Stercobilinogen > Stercobilin
- Reabsorption
- Site
- Unconjugated: Passively in Small Intestine & Colon
- Conjugated: Actively in Terminal Ileum
- Urobilinogen > Urobilin
- Urobilin – Yellow Color of Urine
- Site
- Delta Bilirubin
- Conjugated Bilirubin Bound to Albumin
- 18 Day Half-Life – Long Time to Clear When Chronically Elevated
Bile Contents
- Water (97%)
- Rapid Concentration
- NaCl – Active Absorption (Na/K ATPase)
- Water – Passive Resorption
- Bile Salts (0.7%)
- Function: Emulsifies Fat, Forming Micelles
- Bile Acids
- Source: Cholesterol Breakdown
- Primary Bile Acids
- Cholic & Chenodeoxycholic Mn
- Produced in Liver
- Secondary Bile Acids
- Deoxycholic & Lithocholic
- Transformed by Bacteria in Gut
- Recycled Through Enterohepatic Circulation
- Bile Salt: Bile Acid (Primary or Secondary) Conjugated with Taurine & Glycine
- Improve Water Solubility
- Allow Secretion in Bile
- Cholecystectomy Effects:
- Minimal Effect on Bile Acid Secretion
- Increased Enterohepatic Bile Salt Circulation
- Fats (0.5%)
- Lecithin
- Phospholipid
- Function: Emulsifies Fat & Solubilizes Cholesterol
- Cholesterol
- Fatty Acids
- Lecithin
- Bilirubin (0.2%)
- *See Above
- Inorganic Salts
Hormones
- Bile Excretion
- Increased: Secretin #1, CCK, Parasympathetic (Vagus) Input
- Decreased: Somatostatin, Sympathetic (Splanchnic) Input
- Gallbladder Contraction
- CCK: Constant/Steady Contraction
- Motilin: Stimulates Contraction in Fasting State
- Parasympathetic (Vagus) Input Stimulates Contraction
- Sphincter of Oddi Control
- Morphine: Contracts
- Glucagon: Relaxes
- *See General Abdomen: GI Hormones
Mnemonic
Primary vs Secondary Bile Salts
- “C-Comes First”
- Cholic & Chenodeoxycholic are Primary Bile Salts
- Deoxycholic & Lithocholic are Secondary Bile Salts
References
- Wikimedia Commons (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)
- Perera E, Bhatt S, Dogra VS. Cystic duct remnant syndrome. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2011;1:2. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)