Oncology: Hereditary Cancer Syndromes
General Syndromes
Syndromes
- Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
- PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndromes:
- Cowden Syndrome
- Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome
- Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome
- Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
- Ataxia-Telangiectasia
- Von Hippel Lindau Syndrome
- Muir-Torre Syndrome
- Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer
- Neurofibromatosis Type 1
- Neurofibromatosis Type 2
- Tuberous Sclerosis
- Colorectal Cancer & Polyposis Syndromes
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
- Lynch Syndrome (Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colon Cancer/HNPCC)
- Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome (JPS/Familial Juvenile Polyposis)
- MUT Y Homolog (MUTYH)-Associated Polyposis (MAP)
- Serrated Polyposis Syndrome (SPS)/Hyperplastic Polyposis Syndrome (HPS)
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
- Mutation: p53
- CHEK2 Has Also Been Associated
- Often See Multiple Childhood Tumors
- Strongest Associations: Mn
- Sarcomas (Osteosarcoma & Soft Tissue Sarcoma)
- Breast Cancer
- Brain Cancer
- Leukemia
- Adrenocortical Tumors
- Other Increased Risks: Melanoma, Stomach, Colon, Pancreas, Esophagus, Lung, Gonadal Germ Cell & Wilms’ Tumor
- Definition (Must Have All):
- Proband Diagnosed with Sarcoma Before Age 45
- First-Degree Relative Diagnosed with Any Cancer Before Age 45
- Additional First- or Second-Degree Relative with Either a Sarcoma at Any Age or Any Cancer Before Age 45
- Surveillance:
- Breast MRI Every Year, Starting at Age 20
- Brain MRI Every Year, Starting at Age 18 (From Birth if High-Risk p53 Variant)
- Colonoscopy Every 2-5 Years, Starting at Age 18-25 (*Debated)
PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndromes
- Mutation: PTEN Mn
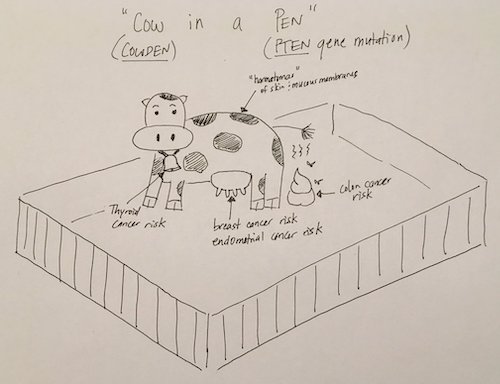
- Cowden Syndrome
- Most Common PTEN Syndrome
- Associations: Diffuse Hamartomas Throughout the GI Tract Mn
- Breast
- Endometrium
- Kidney
- Colorectal
- Thyroid
- Surveillance:
- Physical Exam Every Year, Starting at Age 18
- Thyroid US Every Year, Starting at Age 7
- Colonoscopy Every 5 Years, Starting at Age 35
- Renal US Every 1-2 Years, Starting at Age 40
- Breast MRI or Mammogram Every Year, Starting at Age 30-35
- Random Endometrial Bx Every 1-2 Years
- Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome
- Associations:
- GI Polyposis (Hamartomas)
- Hemangiomas
- Pigmented Penile Macules
- Macrocephaly
- Mental Retardation
- Associations:
- Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome
- Associations:
- GI Polyposis (Hamartomas)
- Alopecia
- Cutaneous Hyperpigmentation
- Onychodystrophy (Dystrophic Nails)
- Associations:
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
- Mutation: STK11 Mn
- Associations:
- GI Hamartomas
- Small Bowel (60-90% Most Common) – Classically in the Jejunum
- Stomach (15-30%)
- Colon (50-64%)
- Melanin Spots of Buccal Mucosa
- Breast Cancer
- Uterine/Cervical Cancer
- Testicular Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancer
- GI Hamartomas
- Diagnosis: (≥ 2 Of):
- ≥ 2 Peutz-Jeghers-Type Hamartomatous Polyps of the GI Tract
- Mucocutaneous Hyperpigmentation
- Family History of Peutz-Jeghers
- Surveillance:
- Baseline Triple-Endoscopy at Age 8 (Colonoscopy, EGD & Video Capsule)
- If Polyps Founds: Repeat Every 2-3 Years
- If Polyps Not Found: Repeat at Age 18 & Every 2-3 Years After
- Breast MRI Every Year, Starting at Age 30
- EUS or MRCP Every 1-2 Years, Starting at Age 30-35
- Pelvic Exams:
- Testicular Exam Every Year Starting at Age 10
- Pelvic/Pap Smear Every Year Starting at Age 18-21
- Baseline Triple-Endoscopy at Age 8 (Colonoscopy, EGD & Video Capsule)
- No Indication for Prophylactic Colectomy
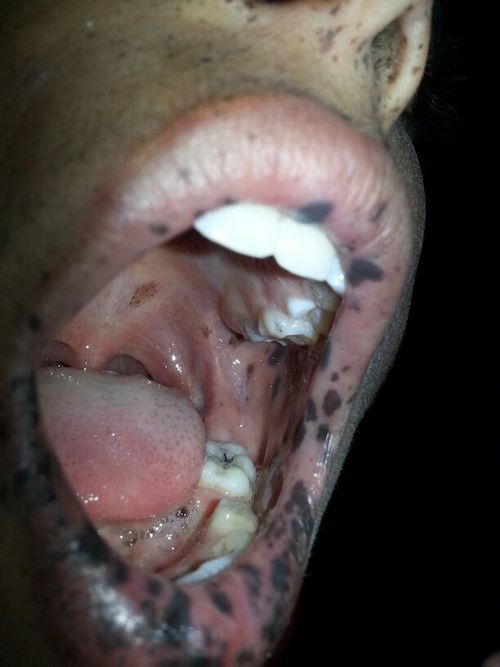
Melanin Spots of Buccal Mucosa 1
Ataxia-Telangiectasia
- Mutation: ATM
- Associations:
- Progressive Cerebellar Degeneration
- Oculocutaneous Telangiectasia
- Immunodeficiency
- Neurologic Vasculo-Cutaneous Findings
- Breast Cancer
- Leukemia
- Surveillance:
- Breast MRI Every Year, Starting at Age 25
Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome
- Mutation: VHL Gene (Upregulation of VEGF)
- Autosomal Dominant
- Associations:
- CNS Tumors (Cerebellar Hemangioblastomas)
- Retinal Hemangioblastomas
- Clear Cell RCC (Most Common Cause of Death)
- Pheochromocytoma
- Surveillance:
- Physical Exam Every Year, Starting at Birth
- Eye/Retinal Exam Every 6-12 Months, Starting at Birth
- Plasma/Urinary Metanephrines Every Year, Starting at Age 5
- MRI Brain & Spine Every 2 Years, Starting at Age 11
- Audiology Assessment Every 2 Years, Starting at Age 11
- US/MRI Abdomen Every 1-2 Years Starting at Age 15
Muir-Torre Syndrome
- Mutation: MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 or PMS2
- MUTYH Has Also Been Associated (Type 2)
- Associations:
- Sebaceous Skin Tumors
- Visceral Cancers:
- Colorectal Cancer – Most Common Visceral Tumor
- Urogenital Tract
- Breast Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Gastric Cancer
- Lung Cancer
Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer
- Mutation: Cadherin 1 (CDH1)
- CTNNA1 Less Commonly Associated
- Associations:
- Gastric CA
- Breast CA
- Prophylactic Surgery:
- Recommended Prophylactic Total Gastrectomy Between Ages 18-40 Years
- May Consider Earlier Surgery for Family History of Gastric Cancer Prior to Age 25
- Consider Prophylactic Mastectomy
- Recommended Prophylactic Total Gastrectomy Between Ages 18-40 Years
- Surveillance:
- Colonoscopy Every Year if Gastrectomy Refused/Deferred
- Breast MRI Every Year, Starting at Age 30
Neurofibromatosis Type 1
- Mutation: NF1
- Associations:
- Café au Lait Spots – Flat Hyperpigmented Macules
- Appear in Childhood & Fade Later in Life
- Neurofibromas & CNS Tumors
- Iris Hamartomas (Lisch Nodules)
- Café au Lait Spots – Flat Hyperpigmented Macules
Neurofibromatosis Type 2
- Mutation: NF2
- Associations:
- Bilateral Vestibular Schwannomas – Most Common
- Intracranial Meningiomas
- Spinal Tumors
- Cataracts
- Cutaneous Tumors & Plaques
Tuberous Sclerosis
- Mutation: TSC1 or TSC2
- Associations:
- Ash Leaf Spots
- Fascial Angiofibroma of the Malar Regions
- CNS Hamartomas
- Tuberous Sclerosis-Associated Neuropsychiatric Disorders (TAND):
- Epilepsy
- Cognitive Deficits
- Autism
- Behavioral Problems
- Cardiac Rhabdomyoma
- Kidney Tumors
Colorectal Cancer & Polyposis Syndromes
- Other Syndromes:
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP)
- Lynch Syndrome (Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colon Cancer/HNPCC)
- Juvenile Polyposis Syndrome (JPS/Familial Juvenile Polyposis)
- MUT Y Homolog (MUTYH)-Associated Polyposis (MAP)
- Serrated Polyposis Syndrome (SPS)/Hyperplastic Polyposis Syndrome (HPS)
- *See Oncology: Colorectal Cancer & Polyposis Syndromes
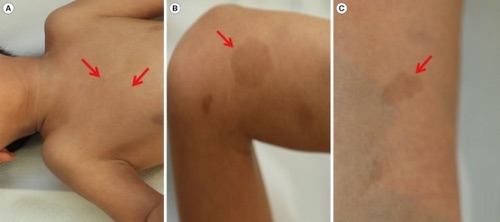
Cafe au Lait Spots 2
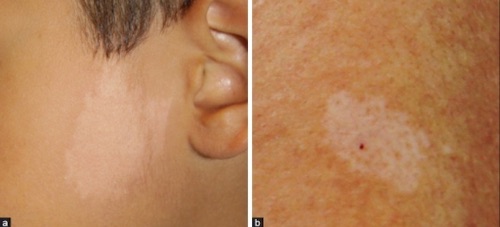
Ash Leaf Spots 3
Comparisons
Breast & Endometrial Cancer
Other Considerations
| Breast | Endometrium | Colorectal | Other | |
| Li-Fraumeni | X | CNS, Adrenal, Sarcoma, Leukemia & Many Others | ||
| ATM | X | Leukemia & Vaso-Cutaneous Findings | ||
| Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer | X | Breast Cancer | ||
| Cowden | X | X | X | Thyroid & Kidney |
| Peutz-Jeghers | X | X | X | Melanin Spots, Pancreas & Testicle |
| Muir-Torre | X | X | X | Other Urogenital Tract & Sebaceous Skin Tumors |
| HNPCC | X | X |
- VHL Has Neither Colorectal or Breast Cancer
- Pancreatic Cancer Primarily in Peutz-Jeghers or Li-Fraumeni
Mnemonics
Li-Fraumeni Syndrome
- Also Known as SBLA Syndrome
- S – Sarcoma
- B – Breast & Brain
- L – Leukemia
- A – Adrenocortical
PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndromes
- “Brr!” (B.R.R.) Cold “Canada” “Cows” are Kept Out in Pens (PTEN)
- Cowden Syndrome
- Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome
- Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome
Cowden Syndrome Associations 4
Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome
- Mutation: STK11
- Buccal Mucosa Spots Look Like a Mouth Filled with “Skittles” – STK11
References
- Sarhan A. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)
- Rim JH, Chung HJ, Shin S, Park SJ, Choi JR. Isodicentric Chromosome 15 Syndrome in a Korean Patient With Café-au-lait Spots. Ann Lab Med. 2015 Jul;35(4):474-6. (License: CC BY-NC-3.0)
- van Geel N, Speeckaert M, Chevolet I, De Schepper S, Lapeere H, Boone B, Speeckaert R. Hypomelanoses in children. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2013 Apr;6(2):65-72. (License: CC BY-NC-SA-3.0)
- @RadOncMnemonics. Twitter.