Breast: Invasive Carcinoma
Invasive Carcinoma
Basics
- Risk in United States:
- Women: 12% (1 in 8)
- Men: 0.13%
- Time of Progression from a Single-Cell to a 1 cm Tumor: 5-7 Years
- Average Survival if Untreated: 2-3 Years
- Average Risk of Developing a Second Breast Cancer in the Contralateral Breast: 0.2-0.5% Per Year
- Sites of Metastasis:
- Bone – Most Common
- Lung
- Brain
- Liver
Histology of Invasive Carcinoma
- Primary Types:
- Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC): Proliferation of Lobule Cells with Basement Membrane Invasion
- 5-10% of All Invasive Breast Lesions
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma (IDC): Proliferation of Ductal Cells with Basement Membrane Invasion
- 70-80% of All Invasive Breast Lesions
- Invasive Lobular Carcinoma (ILC): Proliferation of Lobule Cells with Basement Membrane Invasion
- Less Common Types:
- Tubular Carcinoma (2-20%) – Well-Differentiated, Favorable Prognosis, Rare Mets & Near 100% Survival
- Mucinous (Colloid) Carcinoma (1-2%) – Well-Differentiated & Favorable Prognosis
- Medullary Carcinoma (1-10%) – Somewhat Favorable Prognosis Despite Poor Differentiation (High-Grade), Associated with BRCA I
- Micropapillary Carcinoma – Particularly Aggressive with Worse Prognosis & High Risk for Nodal Metastases Even if Small
- Tubulolobular Carcinoma
- Metaplastic Carcinoma
- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
- Secretory Carcinoma
- Apocrine Carcinoma
Risk Factors
Genetic Mutations
Molecular Receptors
Diagnosis
- *See Breast: Breast Mass Evaluation
- Location Description:
- Multifocal: Multiple Foci in Same Quadrant
- Multicentric: Involves Multiple Quadrants
- Increased Risk if Central & Subareolar
- Pathology:
- ILC: Small Cells Infiltrate Stroma & Adipose Tissue in a Single-File Pattern
- Grow in Linear Plane & Infiltrate Between Tissue Planes Rather Than Distorting
- Cells are Negative for E-Cadherin (Epithelial)
- IDC: Cords & Nests of Tumor Cells with Varying Gland Formation & Fibrotic Response
- Cells are Positive for E-Cadherin
- ILC: Small Cells Infiltrate Stroma & Adipose Tissue in a Single-File Pattern
- Difficult to Detect on Frozen Section (Cells Similar to Lymphocytes)
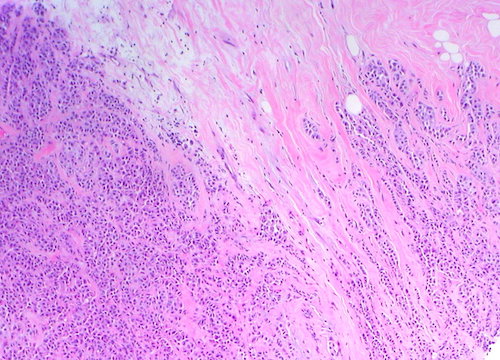
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma 1
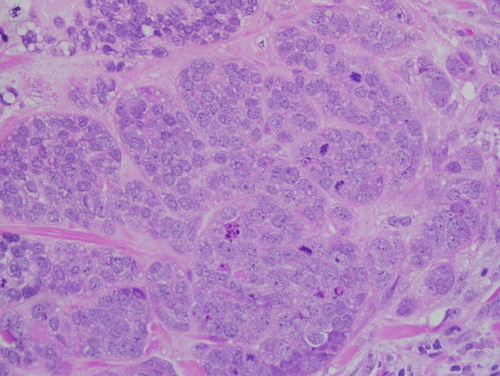
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma 2
TNM Staging
- TNM
| T | N | M | |
| 0 | No Evidence of Primary (is – In Situ) | None | None |
| 1 | < 2 cm T1mi: ≤ 1 mm T1a: > 1 mm
T1b: > 5 mm T1c: > 10 mm |
N1mi: Micrometastases (About 200 Cells, 0.2-2.0 mm)
N1a: 1-3 Axillary Lymph Node Metastaseswith At Least One ≥ 2.0 mm N1b: Mets in Ipsilateral Internal Mammary Sentinel Nodes N1c: Both N1a & N1b |
Distant Mets |
| 2 | > 2 cm | N2a: 4-9 Axillary Lymph Node Metastaseswith At Least One ≥ 2.0 mm
N2b: Positive Internal Mammary Nodes by Imaging with Pathologically Negative Axillary Nodes |
|
| 3 | > 5 cm | N3a: ≥ 10 Axillary Lymph Node Metastases or Infraclavicular Lymph Node Metastases
N3b: N1a or N2a with cN2b (Positive Internal Mammary Nodes by Imaging); or N2a with N1b N3c: Mets in Ipsilateral Supraclavicular Lymph Nodes |
|
| 4 | T4a: Extension into Chest Wall (Not Muscle)
T4b: Skin Ulceration or Edema (Peau d’Orange) T4c: Both T4a & T4b T4d: Inflammatory Carcinoma *Invasion of Dermis Alone Does Not Qualify as T4 |
- Stage
| T | N | M | ||
| I | A | T1 | N0 | M0 |
| B | T0-1 | N1mi | M0 | |
| II | A | T0-1 | N1 | M0 |
| T2 | N0 | M0 | ||
| B | T2 | N1 | M0 | |
| T3 | N0 | M0 | ||
| III | A | T0-2 | N2 | M0 |
| T3 | N1-2 | M0 | ||
| B | T4 | N0-2 | M0 | |
| C | Any T | N3 | M0 | |
| IV | Any T | Any N | M1 | |
Treatment
- Primary Treatment: Breast-Conserving Therapy (BCT) or Mastectomy
- Margin: Negative Margin (“No Ink on Tumor”)
- Positive Margin: Re-Excise the Margin
- If Unsure Which Margin is Positive: Re-Excise All 6 Margins
- Positive Margin: Re-Excise the Margin
- Lymph Node Management:
- Both Options Require Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SLNB)
- *See Breast: Lymph Node Management
- Breast-Conserving Therapy (BCT) Generally Requires Adjuvant Radiation Therapy
- Contraindications to Breast-Conserving Therapy (BCT):
- Patient Preference
- Other Contraindications: *See Breast: Surgical Treatment
- Margin: Negative Margin (“No Ink on Tumor”)
- Locally Advanced (T3-T4): Consider Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy to Downstage
- Stage IV (M1): Palliative Chemotherapy
- Adjuvant Therapy:
- Radiation Therapy: *See Breast: Radiation Therapy (RT)
- Chemotherapy: *See Breast: Chemotherapy
- Hormonal Therapy: *See Breast: Hormonal/Endocrine Therapy (HT)
Special Populations
- Gestational (Pregnancy-Associated) Breast Cancer
- Male Breast Cancer
References
- Uthman E. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-2.0)
- Wu D. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-3.0)