Trauma: Burns
Thermal Burns
Thickness
| Degree | Thickness | Depth | Sensation | Blanch | Presentation |
| 1st | Superficial | Epidermis | Pain | Yes | Erythema |
| 2nd | Superficial Partial | Superficial Dermis | Pain | Yes | Blister in 24 Hours, Weeps |
| Deep Partial | Deep Dermis | Decreased | No | Loss of Hair Follicles, Mottled Color, Blister | |
| 3rd | Full | Subcutaneous | Painless | No | Leathery, Charred |
| 4th | To Muscle & Bone |
- Superficial & Superficial Partial Heal by Epithelialization
- Primarily from Hair Follicles but Also from Skin Edges
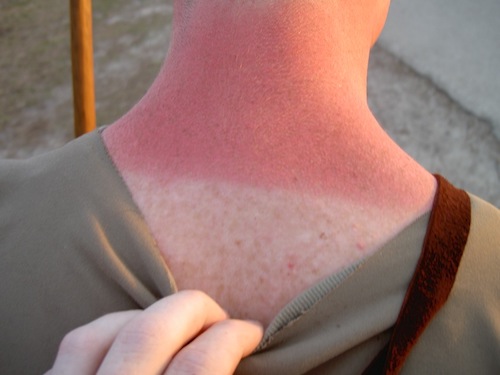
Superficial Thickness 1
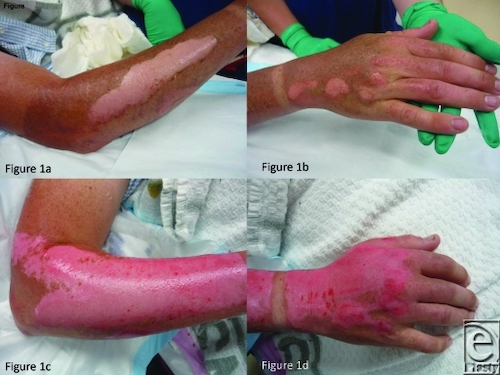
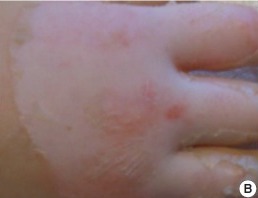
Superficial Partial Thickness 2
Deep Partial Thickness 3
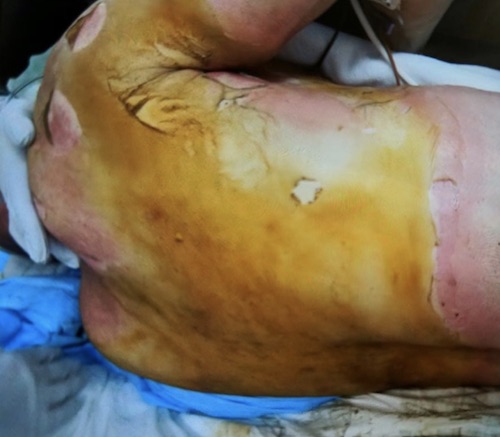
Full Thickness
Body Surface Area (BSA)
- Predict by “Rule of 9’s”
- Add 9% for Each:
- Head
- Chest
- Abdomen
- Upper Back
- Lower Back
- Right Arm
- Left Arm
- Right Upper Leg
- Left Upper Leg
- Right Lower Leg
- Left Lower Leg
- Add 1% for the Perineum
- Approximately 1% Per Palmar Area
- Add 9% for Each:
- Young Children
- Differences:
- Head Doubled (18%)
- Legs are 7% Per Section
- None for Genitals
- Differences:
Baux Score
- Predicts Mortality After Burn Injury
- Baux Score = Age + %TBSA
- Modified/Revised Baux Score = Add 17 if an Inhalational Injury Present
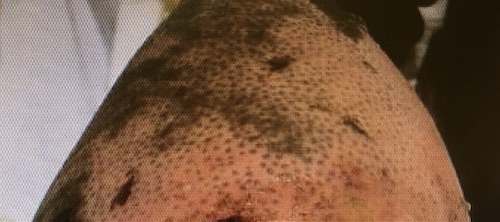
Healing from the Hair Follicles
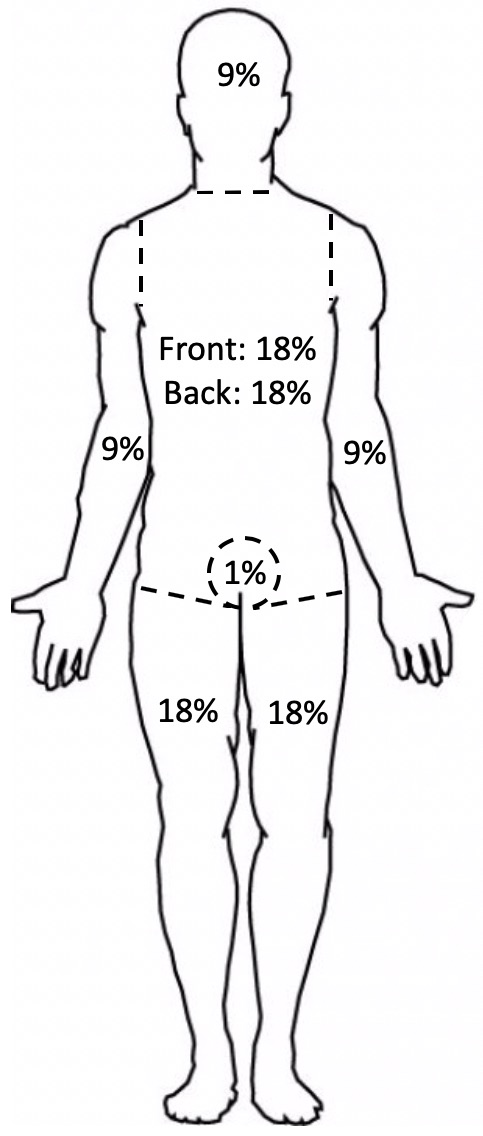
BSA Rule of 9’s
Treatment
Initial Fluid Replacement
- Formulas:
- Parkland Formula
- Initial Fluid for First 24 Hours if > 20% BSA
- Total Volume = BSA x Weight (kg) x 4 cc/kg/BSA
- BSA Used as Whole Number, Not Decimal (25% = 25; Not 0.25)
- Burns ≥ 2nd Degree
- 1st Degree Do Not Count
- Administration:
- Give First Half Over 8 Hours
- Give Second Half Over 16 Hours
- Modified Brooke Formula
- Same as Parkland but uses 2 cc/kg/BSA Instead of 4 cc/kg/BSA
- Minimizes Risk of Over Resuscitation
- Rule of Ten
- Initial Hourly Rate = 10 x BSA
- Used to Approximate the Modified Brooke Formula
- *Assumes an 80 kg Patient Weight for Calculation
- Parkland Formula
- For Pediatrics Use 3-4 cc/kg/BSA
- Use LR for First 24 Hours
- Formulas Serve to Approximate the Initial Rate but Should Be Adjusted by UOP Once Able
- Goal UOP: 0.5 cc/kg/hr
Management
- Initial Treatment: ABC’s – Do Not Become Distracted by the Burn
- If Transferring: Dressing Warm & Dry – Allow Thorough Examination on Arrival
- Definitive Treatment:
- Superficial: Salves/Ointment
- Superficial Partial: Clean & Dressing
- Deep Partial & Full Thickness: Debride & Skin Graft in 24-48 Hours
- Best Indicator of Viability: Punctate Bleeding
- Skin Graft: *See Skin & Soft Tissue: Plastics & Tissue Transfer
- Sensitive Areas
- Face, Genitals, Palms & Soles: Defer for First Week
- Hands: Set in Extension
- Superficial: Splint
- Deep: Immobilize Post FTSG
Antibiotics
- Topical Agents:
- Bacitracin & Neomycin
- Primarily Used on Face
- Covers: Poor GNR Coverage
- Painless
- Side Effects: Nephrotoxicity (Particularly if Given by Intramuscular Injection)
- Silver Sulfadiazine (Silvadene)
- Most Commonly Used in Partial Thickness
- Covers: Effective for Candida
- Avoid with Sulfa Allergy
- Painless
- Side Effects: Neutropenia & Thrombocytopenia Mn
- Mafenide Acetate (Sulfamylon)
- Silver Nitrate
- Side Effects: Electrolyte Imbalance (Na, Cl & K) Mn
- Mupirocin
- Covers: Best for MRSA
- Bacitracin & Neomycin
- Systemic Agents:
- Not for Prophylaxis
- Give if Diagnosed Infection
Burn Excision/Debridement
- Tangential Excision
- Sequential Excision of Eschar Until Punctate Bleeding Seen
- Allows Identification of Healthy Tissue to Optimize Wound for Reconstruction
- Disadvantage: Large Amount of Blood Loss
- Contraindicated in Hemodynamically Unstable Patients
- Fascial Excision
- Excision of Eschar & Underlying Subcutaneous Tissue to the Muscle Fascia Using Electrocautery
- Limits Bleeding
Escharotomy
- Done at Bedside
- Incisions:
- Extremity: Vertical (Not Horizontal)
- Torso: Square Over Anterior Chest
- Transverse Incisions Over Chest & Abdomen
- Vertical Incisions Along the Anterior Axillary Lines
- Indications:
- Deep Circumferential
- Signs of Compromised Distal Blood Flow
- Difficult Ventilation with Diffuse Torso Burns
- In General, Only Incision of the Eschar is Required & Able to Spare Fascia
- Concomitant Fasciotomy is Indicated if Compartment Syndrome Suspected
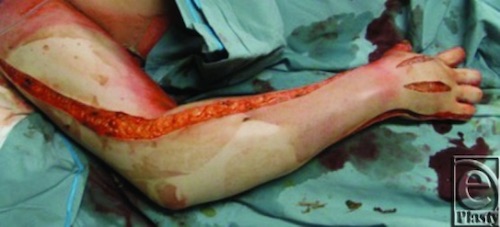
Vertical Arm Escharotomy 4
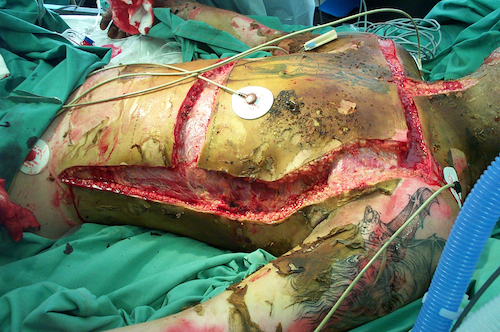
Torso “Roman Breastplate” Escharotomy 5
Admission/Transfer Criteria
- Burn Center Transfer Criteria
- 2nd Degree Burns
- Age < 10: > 10% BSA
- Age 10-50: > 20% BSA
- Age > 50: > 10% BSA
- Any to Face, Hands, Feet, Perineum or Major Joints
- 3rd Degree Burns
- > 5% BSA
- Other Factors:
- Any Electrical or Chemical Burns
- Any Concomitant Inhalation Injury or Multiple Trauma
- 2nd Degree Burns
- Other Admission Criteria
- Abuse/Neglect
- Special Needs: Low SES or Long-Term Rehab
- Concomitant Preexisting Medical Conditions
Complications
Wound Infection
- Risk Factors from Burn: Impaired Granulocyte Chemotaxis & Cell-Mediated Immunity
- Organisms: Pseudomonas (Most Common), Staphylococcus
- Candida – Increased from Topical Agents
- HSV – Most Common Viral Infection
- Best Dx: Bx
- Must be > 105 to be Considered Burn Wound Infection
- Tx:
- Just Surrounding Cellulitis: IV ABX
- More Invasive: IV ABX & Excision with Allograft (Not Autograft)
Healing Issues
- Hypertrophic Scarring
- From Increased Neovascularization
- Tx: Steroid Injection (#1), Wait 1 Year Before Surgical Resection
- Marjolin’s Ulcer
- Aggressive Ulcerating SCC From Chronic Wounds/Burns
- *See Skin & Soft Tissue: Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
Airway Issues
- Severe Inhalation Injury
- Airway Damage is From Inhaled Toxins
- Signs: Face Burn, Singed Nasal Hairs, Soot in Nares
- Dx: Direct Laryngoscopy of Posterior Oropharynx or Bronchoscopy
- Intubation Indications:
- Posterior Pharyngeal Swelling
- Mucosal Sloughing
- Carbonaceous Sputum Below Vocal Cords
- Pneumonia (PNA)
- Most Common Infection in Large Burns
- Most Common Cause of Death in Large Burns
- #1 Risk Factor: Inhalation Injury
- Carbon Monoxide (CO) Poisoning
- Tasteless Odorless Gas Formed from Incomplete Combustion of Fossil Fuels
- Toxicity Arises from Smoke Inhalation
- Carboxyhemoglobin (CO Bound to Hgb)
- CO Binds to Hemoglobin with a Higher (200x) Affinity than Oxygen
- Causes Hypoxia with a Left-Shift in the Oxygen-Dissociation Curve
- Pulse Oximetry Falsely Elevated
- Presentation:
- Headache
- Nausea & Vomiting
- Confusion & Coma
- Diagnosis: Carboxyhemoglobin Level
- Normal Levels: 5% (Nonsmokers), 10% (Smokers)
- Confusion Occurs Once ≥ 20%
- Brain Death Occurs Once ≥ 60%
- Tx: 100% Oxygen by Nonrebreather Mask
- Most Effective Form: Hyperbaric Oxygen Chamber
- Tasteless Odorless Gas Formed from Incomplete Combustion of Fossil Fuels
Soot in Airway 6
Other Issues
- Avoid Succinylcholine – Increased Hyperkalemia Response with Cardiac Arrest
- Electrolyte Changes
- Hypernatremia (#1 Most Common)
- Initially Low from Extracellular Depletion with Changes in Cellular Permeability
- Then High Due to Insensible Loss & Inadequate Resuscitation
- Hyperkalemia
- From Severe Tissue Necrosis
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypomagnesemia
- Hypernatremia (#1 Most Common)
- Neuro
- Seizure
- From Na Imbalance
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- From Small Vessel Injury/Demyelination
- Seizure
- Ophtho
- Ectopia
- Displacement from Contraction
- Tx: Release
- Corneal Abrasion
- Dx: Fluorescein Staining
- Tx: Topical ABX
- Symblepharon
- Lid Stuck to Eye
- Tx: Glass Rod Release
- Ectopia
- Muscular
- Tendon Heterotopic Ossification
- Tx: PT
- Rhabdomyolysis
- Tendon Heterotopic Ossification
- Renal Failure
- From Rhabdomyolysis & Volume Loss
- Tx: IVF & Alkalinize Urine
Other Burns
Chemical Burns
- Primary Treatment: Copious Saline Irrigation
- Hydrofluoric Acid
- Seen in Cleaning Agents, Rust Removers, Batteries & Fertilizers
- Cause Calcium Chelation & Arrhythmias
- Initial Treatment: Topical Calcium Gluconate (After Irrigation)
Electric Shock
- Current Types
- Direct (Battery)
- Single Large Contraction
- Throw Victim Away
- Alternating (Power Line)
- Repetitive Contractions
- Often Grip with Prolonged Exposure (Flexor Stronger then Extensor)
- Direct (Battery)
- Penetration
- Skin Marks Vastly Underestimate Severity
- See Significant Rhabdomyolysis
- Adipose Has High Resistance to Electricity
- Obese Have Increased Deep Thermal Burns
- Skin Marks Vastly Underestimate Severity
- Most Common Cause of Death: Arrhythmia
Mnemonics
Topical Antibiotic Side Effects
- Mafenide Acetate (MA): Metabolic Acidosis
- Silver Nitr-Ate: Na+
- Silver (Not Na): White Cells
Mafenide Acetate Has Good Eschar Penetration
- Acid Burns Through Eschars
References
- Kates P. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-2.0)
- Greenwood JE. A Randomized, Prospective Study of the Treatment of Superficial Partial-Thickness Burns: AWBAT-S Versus Biobrane. Eplasty. 2011 Feb 24;11:e10. (License: CC BY-2.0)
- Toussaint J, Singer AJ. The evaluation and management of thermal injuries: 2014 update. Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2014 Sep 30;1(1):8-18.(License: CC BY-NC-3.0)
- Schulze SM, Weeks D, Choo J, Cooney D, Moore AL, Sebens M, Neumeister MW, Wilhelmi BJ. Amputation Following Hand Escharotomy in Patients with Burn Injury. Eplasty. 2016 Mar 2;16:e13. (License: CC BY-2.0)
- Sarwark J. The Escharotomy. EM Curious. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Milner SM, Fauerbach JA, Hahn A, Price LA, Ware L, Krout K, Panter E, Pharm NK, Pfeiffer J, Nguyen H, Sood G, Dhanjani K, McKeon G, Gerold K. Cody. Eplasty. 2015 Aug 6;15:e35. (License: CC BY-2.0)