Esophagus: Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Basics
General
- Reflux of Gastric Acid into the Esophagus
- The Most Common GI Diagnosis in the West
- 10-20% Prevalence
Risk Factors
- Smoking
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
- Trigger Foods (Fatty/Fried)
- Gastroparesis
- Obesity
- Hiatal Hernia
- Pregnancy
Symptoms
- Typical Symptoms:
- Pyrosis (Heartburn)
- 30-60 Min After Meals
- Worse When Supine
- Regurgitation (Perception of Refluxed Gastric Acid into the Mouth)
- Epigastric Pain
- Pyrosis (Heartburn)
- Atypical Symptoms:
- Water Brash (Increased Saliva Production Mixed with Gastric Acid in the Mouth)
- Odynophagia (Painful Swallowing)
- Globus Sensation (Perception of a Lump in the Throat)
- Cough
- Aspiration
- Wheezing
- Hoarse Voice
Alarm Symptoms
- Alarm Symptoms:
- Dysphagia
- Weight Loss, Early Satiety or Anorexia
- GI Bleed (Hematemesis/Melena) or Anemia
- Persistent Vomiting
- Need EGD to Evaluate for Cancer
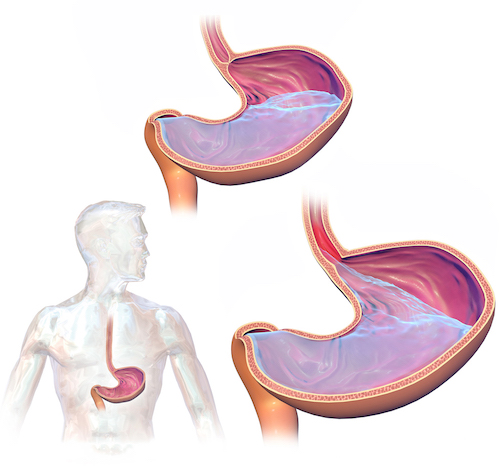
GERD 1
Complications
Erosive Esophagitis
Barrett’s Esophagus
Esophageal Stricture
Extraesophageal Complications
- Asthma
- Mechanisms: Increased Vagal Tone, Bronchial Reactivity & Microaspiration
- Laryngotracheal Stenosis
- Chronic Laryngitis
- Chronic Cough
- Dental Erosions
Management
Immediate Relief
Initial Therapy
- Initial Tx: PPI 3-4 Weeks & Lifestyle Modifications
- Lifestyle Modifications: Weight Loss & Avoid Triggering Foods
- Medication:
- Initial Dose: PPI Once Daily
- If Fails & Diagnosis Confirmed: Increase to Twice Daily or Add H2 Blocker
- *See Pharmacology & Anesthesia: Anti-Reflux Medication
- 99% Effective
- If Fails: Diagnostic Testing
- Failure Defined as No Improvement After 8-12 Weeks
Diagnostic Testing
- pH Probe
- First Test to Diagnose (But Not Mandatory)
- DeMeester Score
- Components:
- Percent Total Time pH < 4
- Percent Upright Time pH < 4
- Percent Supine Time pH < 4
- Number of Reflux Episodes Total
- Number of Reflux Episode > 5 min
- Longest Reflux Episode
- Score > 14.72 Indicates Reflux
- Components:
- Upper Endoscopy
- Not Required for GERD Diagnosis
- Evaluates Hiatal Hernia, Strictures, Esophagitis, Metaplasia & Malignancy
- Manometry
- To Rule Out Underlying Motility Disorder
- Indications:
- If Upper Endoscopy Normal
- Required If Planning Surgery
Antireflux Surgery
- Primary Surgery: Fundoplication
- *See Esophagus: Fundoplication
- Concurrent Dysmotility Requires Partial Fundoplication
- May Consider Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass if Morbidly Obese with Indications for Bariatric Surgery – Small Pouch is Created with Minimal Acid Production
- Indications:
- Failed Medical Management
- GERD Complications (Esophagitis or Stricture)
- PPI Side Effects (Headache, Nausea, Vomiting or Diarrhea)
- Patient Preference
- Poor Compliance
- Contraindications:
- Unable to Tolerate Surgery
- High-Grade Dysplasia or Carcinoma
- Morbid Obesity – Relative Contraindication
- Consider Gastric Bypass
- Best Predictors of Success:
- Typical Symptoms
- Typical Symptoms Resolve in 90% of Patients
- Atypical Symptoms Resolve in 60-70% of Patients
- Symptoms Improved on PPI
- High Esophageal pH
- Typical Symptoms
Other Modern Antireflux Procedures
- Magnetic Sphincter Augmentation (LINX Device)
- Ring Made of Magnets Placed Around the LES
- Increases LES Pressure while Closed
- Can Open with Pressure while Swallowing to Permit Food Passage
- Exact Indications Poorly Defined
- Benefits Over Fundoplication:
- Shorter Surgery & Faster Recovery
- Easily Reversible
- Does Not Permanently Alter Stomach Anatomy
- Retains Ability to Belch/Vomit
- Potential Risk for Esophageal Erosion (0.3%)
- Should Eat Frequent Solid Meals Postop to Prevent Scarring Capsule Formation & Resulting Dysphagia
- Ring Made of Magnets Placed Around the LES
- Stretta Procedure
- Endoscopic Controlled Radiofrequency Energy Applied to the LES
- Induces Inflammation, Collagen Deposition & Muscular Thickening
- Transoral Incisionless Fundoplication (TIF)
- Endoscopic Full Thickness Plication
- Partial Fundoplication (200-300-Degrees)
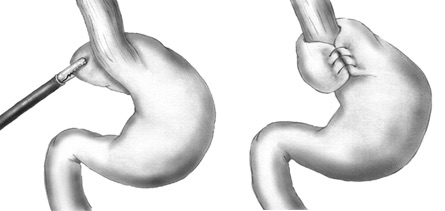
Nissen Fundoplication 2

LINX Device 3
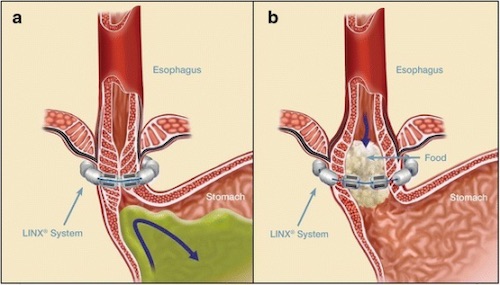
LINX Procedure 3
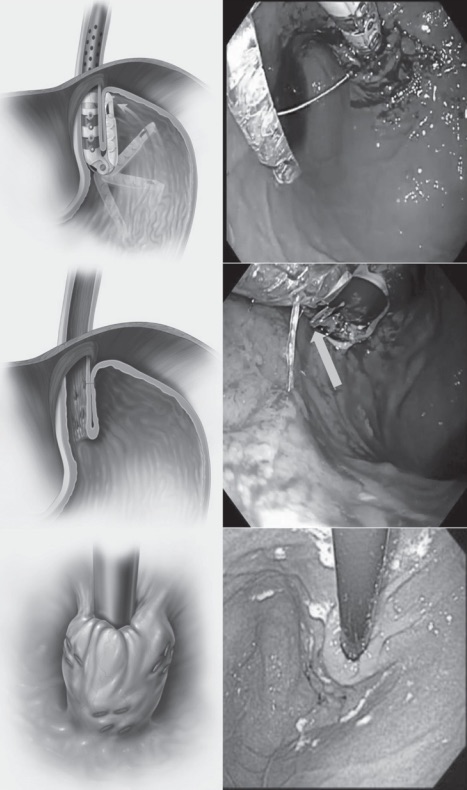
TIF 4
References
- Blaus B. Wikimedia Commons. (License: CC BY-SA-4.0)
- Gray H. Public Domain.
- Sriratanaviriyakul N, Kivler C, Vidovszky TJ, Yoneda KY, Kenyon NJ, Murin S, Louie S. LINX®, a novel treatment for patients with refractory asthma complicated by gastroesophageal reflux disease: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2016 May 24;10(1):124. (License: CC BY-4.0)
- Sami Trad K. Transoral incisionless fundoplication: current status. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2016 Jul;32(4):338-43. (License: CC BY-NC-ND-4.0)